COP28 Head Claims There’s ‘No Science’ Behind Fossil Fuel Phaseout

Original article by JAKE JOHNSON republished from Common Dreams under Creative Commons (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
“This dismisses decades of work by IPCC scientists,” said one expert. “Disgraceful.”
Scientists and climate advocates responded with outrage Sunday to COP28 president Sultan Ahmed Al Jaber’s claim that there is “no science” behind the push to rapidly phase out planet-warming fossil fuels, which Al Jaber’s company is extracting on a large scale .
Al Jaber’s comments, first reported by The Guardian on Sunday, came in response to questioning from Elders chair Mary Robinson during a virtual She Changes Climate discussion. Robinson told Al Jaber that “we’re in an absolute crisis that is hurting women and children more than anyone… and it’s because we have not yet committed to phasing out fossil fuel.”
The COP28 chief and Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) CEO responded dismissively, saying he “accepted to come to this meeting to have a sober and mature conversation” and not to take part in “any discussion that is alarmist,” according to audio published by The Guardian .
“There is no science out there, or no scenario out there, that says that the phaseout of fossil fuel is what’s going to achieve 1.5°C,” Al Jaber added. “Please help me, show me the roadmap for a phaseout of fossil fuel that will allow for sustainable socioeconomic development, unless you want to take the world back into caves.”
That position runs directly counter to the outspoken stance of United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres, who said Friday that “the 1.5°C limit is only possible if we ultimately stop burning all fossil fuels,” arguing that “the science is clear.”
Joelle Gergis, a climate scientist and lead author of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC) Working Group I contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report , called Al Jaber’s remarks “disgraceful.”
“This dismisses decades of work by IPCC scientists,” Gergis wrote on social media.
“‘Sending us back to caves’ is the oldest of fossil fuel industry tropes: it’s verging on climate denial.”
The IPCC, which has synthesized the research of hundreds of climate scientists from around the world, has argued that any successful effort to prevent catastrophic planetary warming “will involve a substantial reduction in fossil fuel use.”
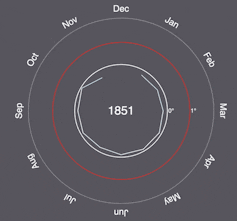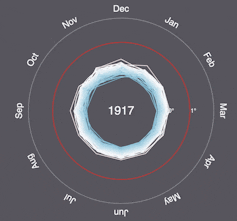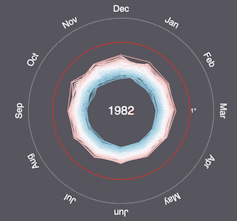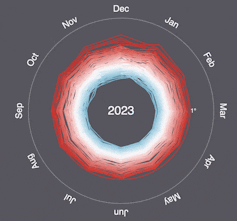
“More than a century of burning fossil fuels as well as unequal and unsustainable energy and land use has led to global warming of 1.1°C above pre-industrial levels,” the IPCC said following the release of its latest report earlier this year. “This has resulted in more frequent and more intense extreme weather events that have caused increasingly dangerous impacts on nature and people in every region of the world.”
Other recent research has warned that rich nations must completely halt oil and gas production by 2034 to give the world a 50% chance of limiting warming to the 1.5°C target set by the Paris Agreement.
Bill Hare, chief executive of Climate Analytics, told The Guardian that Al Jaber’s response to Robinson was “extraordinary, revealing, worrying, and belligerent.”
“‘Sending us back to caves’ is the oldest of fossil fuel industry tropes: it’s verging on climate denial,” said Hare.
Al Jaber’s comments, which he says have been misrepresented , were seen as further confirmation that he is ill-suited to lead a climate summit given his simultaneous role as the top executive at one of the world’s largest fossil fuel firms. A Global Witness analysis released over the weekend found that ADNOC is on track to become the second-largest oil producer in the world by 2050, and Al Jaber has been accused of using his position as COP28 president to pursue oil and gas deals.
“ADNOC plans to produce more oil than any of the ‘Big 5’ supermajors—ExxonMobil, Chevron, Shell, BP, TotalEnergies,” Global Witness found. “In fact, its projected output will positively dwarf that of the European majors; ADNOC’s 35.9 billion barrels is 49% higher alone than the projected 24.1 billion barrels production of Shell, BP, and Total combined.”
On Monday, the COP28 presidency published a summary of the World Climate Action Summit, a gathering of more than 150 heads of state aimed at facilitating coordinated climate action.
The document states that world leaders “highlighted the opportunities to cut emissions in every sector and to accelerate the technology innovation to address scope 3 emissions, as well as the phase-down of fossil fuels in support of a transition consistent with limiting warming to 1.5°C.”
Romain Ioualalen, global policy lead at Oil Change International , said in a statement that “strong support from the leaders’ summit to address fossil fuels in the final COP28 agreement is a promising sign, but it is just good enough.”
“Leaders must raise their ambition above a phase-down, and agree to immediately stop new fossil fuel expansion, and build a fast, full, fair, and funded phaseout of all fossil fuels while rapidly phasing in renewables,” said Ioualalen. “Contrary to the COP28 president’s assertions, the science is abundantly clear that warming will continue as long as we keep producing and burning fossil fuels.”
Original article by JAKE JOHNSON republished from Common Dreams under Creative Commons (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).