Just 36 Companies Drove Half the World’s Climate-Altering Emissions in 2023: New Report
Original article by Sharon Kelly republished from DeSmog.

Companies and states most responsible for climate change are also those working hardest to prevent climate action, new Carbon Majors report finds.
Half of the world’s carbon dioxide emissions in 2023 came from just three dozen companies, according to a new report released today by the Carbon Majors project, with the list dominated by coal, cement, and oil producers.
Saudi Arabia’s Saudi Aramco, the year’s worst offender, drove 4.4 percent of the world’s carbon dioxide pollution alone in 2023, the report found.
Five publicly-traded oil companies — ExxonMobil, Chevron, Shell, TotalEnergies, and BP — combined to produce an additional 4.9 percent of the year’s global carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels, the report adds.
The Carbon Majors database builds on the innovative work published by researcher Richard Heede of the Climate Accountability Institute (CAI) begun in 2013. For the first time, instead of attributing the build-up of industrial carbon dioxide and methane emissions to each of the world’s nations, Heede managed to trace those emissions to 90 specific “carbon major” companies. Last year, the nonprofit think tank InfluenceMap collaborated with CAI to produce major updates to the database — and today’s report marks the first annual update to that report, incorporating global data from 2023.
The year’s top carbon polluters were a mix of investor-owned and state-owned or national companies — but they have one thing in common.
“They’re some of the most obstructive actors towards climate policy,” Emmett Connaire, a senior analyst at the Carbon Majors project and one of the authors of the report, told DeSmog.
“I think it kind of kills the argument from industry that they’re not responsible for their CO2 emissions because we need fossil fuels to grow,” Connaire said, “when they’re the most obstructive and trying to keep up the demand for their products in the face of the overwhelming scientific opinion.”
Eight of the nine public companies most responsible for carbon emissions in 2023 were “highly active or strategic” in their climate lobbying, the report notes. And their lobbying efforts took aim at regulating climate-altering pollution or sought to impede the energy transition.“ Of these 9 companies, 5 score a D or below, indicating unsupportive positions on climate policy,” the new report finds, citing data from InfluenceMap’s LobbyMap database, which grades companies based on their alignment with the Paris Agreement. “The remaining 4 score only slightly higher at C-.”
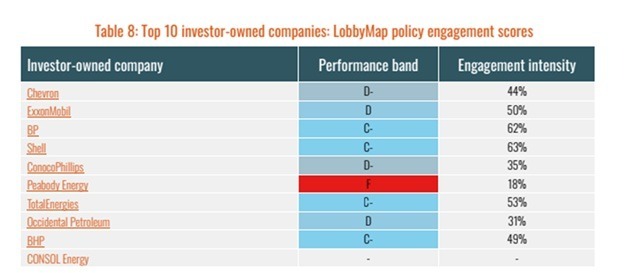
None of the five top oil companies named in the report immediately responded to a request for comment from DeSmog.
Investor-owned companies aren’t the only ones actively fighting to prevent climate action, the Carbon Majors report notes.
“State-owned companies are even more oppositional to climate regulation globally according to LobbyMap research,” the report finds, listing Saudi Aramco, Russia’s Gazprom, Mexico’s Pemex, and China’s CHN Energy among the worst actors.
“The ‘Carbon Majors’ are keeping the world hooked on fossil fuels with no plans to slow production,” former United Nations climate chief and Paris Agreement architect Christiana Figueres said in a response accompanying the report. “While states drag their heels on their Paris Agreement commitments, state-owned companies are dominating global emissions — ignoring the desperate needs of their citizens.”
A sizable majority — 80 percent — of the year’s 20 worst offenders are state-owned, the report found.
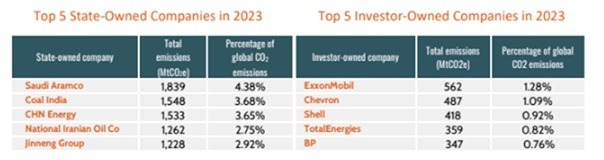
Throughout history, responsibility for driving climate change is concentrated among a strikingly small number of corporations, the report suggests.
Two-thirds of all fossil fuel and cement emissions worldwide from 1750 through 2023 can be traced to just 181 entities, the report finds, adding that one-third of emissions came from just 26 companies.
These findings may have significant legal consequences. During 2024, New York state and Vermont both enacted “Climate Superfund” laws that aim to hold fossil fuel producers and oil refiners responsible for the damage done by their climate-altering products — and the Carbon Majors database is a proposed tool to assess companies’ relative liabilities, according to InfluenceMap. Its earlier findings have been cited in civil lawsuits brought by U.S. cities and counties against fossil fuel producers and an inquiry in the Philippines (which has seen some of the strongest typhoons in recorded history) into corporate responsibility for human rights violations.
The report approaches companies’ contributions to climate change based on production data — meaning that it focuses on the companies that do the drilling and mining (which helps avoid double-counting, Connaire told DeSmog). Those production figures are self-reported by companies but are widely used by governments to assess taxes and by investors in public companies. That methodology means that, for example, natural gas pipeline companies and natural gas utilities aren’t included in the report’s rankings.
Nonetheless, natural gas producers figure among the report’s list of all-time top polluters. That includes the former Chesapeake Energy, which first rose to prominence — and some notoriety — during the shale gas fracking boom only to implode into bankruptcy in 2020. Chesapeake later emerged from bankruptcy and has since merged into the newly formed Expand Energy.
As the Carbon Majors database traces emissions throughout history, it accounts for the effects of mergers and acquisitions in the tumultuous oil industry, known for its booms and busts. “For example, the multiple smaller companies into which the Standard Oil Trust was broken up have evolved to become some of the most recognizable companies in the database today,” the report notes. “Some are direct descendants of Standard Oil, like ExxonMobil, with both Exxon and Mobil as descendants separately, and Chevron. Others have resulted from mergers with descendants of Standard Oil, such as BP and ConocoPhillips.”
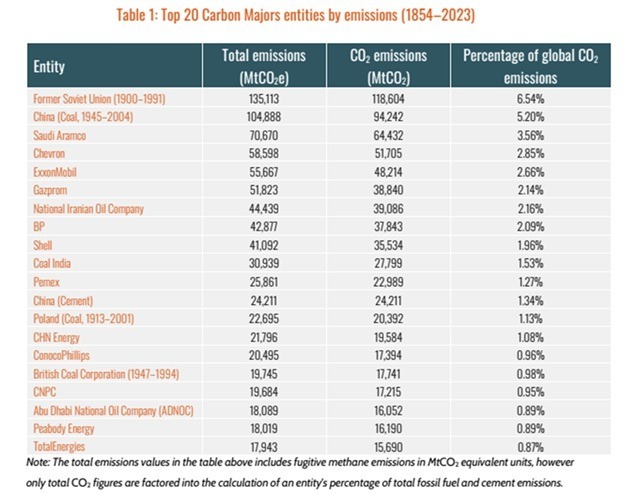
It also calls attention to the importance of coal pollution — not just historically, but also in 2023.
“In 2023, coal remained the largest source of emissions, contributing 41.1 percent of emissions in the database,” the new report finds, “continuing a steady increase since 2016.”
Emissions from the cement industry — also a major driver of carbon pollution — increased significantly in 2023, rising 6.5 percent year-over-year, which the Carbon Majors report noted was “the largest relative rise” found. “Four of the five companies with the greatest relative increases in emissions in 2023 were cement companies — Holcim Group, Heidelberg Materials, UltraTech Cement, and CRH — with cement emissions seeing the largest relative rise among the four commodity types.”
Cement producers aren’t the only ones, however. In fact, emissions from most of the top emitters rose in 2023, the Carbon Majors report found.
“It is truly alarming that the largest fossil fuel companies continue to increase their emissions in the face of worsening natural disasters caused by climate change, disregarding scientific evidence that these emissions are harming us all,” said Tzeporah Berman, founder of the Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty Initiative. “It is clearer than ever that dirty private companies, driven by profits and business as usual, will never choose to self-regulate. Governments around the world must use their power to end fossil fuel expansion and transition their economies before fossil fuel companies destroy the planet.”
Original article by Sharon Kelly republished from DeSmog.





