Big Oil Clouded the Science on Extreme Weather. Now It Faces a Reckoning.
Original article by Emily Sanders, ExxonKnews republished from DeSmog.
As more communities sue oil majors following climate disasters, a collection of evidence reveals the industry’s efforts to deny the link between extreme weather and climate change.

This story was originally published by ExxonKnews.
When Bucks County, Pennsylvania, filed a lawsuit last week against major oil and gas companies for climate damages, Commissioner Chair Diane Ellis-Marseglia pointed to “unprecedented weather events here in Bucks County that have repeatedly put residents and first responders in harm’s way, damaged public and private property and placed undue strain on our infrastructure.” The county argues oil companies’ “campaigns to deceive and mislead the public about the damaging nature of their fossil fuel products” delayed climate action for decades, robbing communities of precious time to mitigate the climate-driven disasters they now face.
One of those disasters occurred last year, when a rainstorm in Bucks County caused deadly flash flooding that swallowed vehicles and killed 7 people, including two children. Scientists said the deluge and its aftermath — not the county’s first “100-year flood” in recent years — are a harbinger of the intense and dangerous rainstorms that a warming climate is making more likely.
As the science connecting climate change to more frequent and severe weather events becomes clearer, there is mounting evidence that members of the fossil fuel industry coordinated to downplay that link — evidence that could be valuable to lawsuits seeking accountability.
Bucks County is just one in a growing list of communities taking legal action against fossil fuel companies in the wake of deadly extreme weather events. Multnomah County, Oregon sued oil, gas, and coal majors after a 2021 heat dome that killed nearly 70 people. On the 10 year anniversary of Superstorm Sandy, New Jersey’s attorney general took Exxon, Chevron, and other oil giants to court, citing the billions of dollars in damage and deaths the hurricane caused in the state. In the first-ever racketeering lawsuit against Big Oil companies, Puerto Rico municipalities are seeking to recover costs incurred by Hurricane Maria.
Fossil fuel majors, these cases argue, should help communities pay for the costs of adapting to and recovering from climate disasters given the industry’s early research into — and subsequent denial of — their products’ harm. “We’re already seeing the human and financial tolls of climate change beginning to mount,” said Commissioner Ellis Marseglia. “If the oil companies’ own data is to be believed, the trend will continue.”
It’s a trend that the fossil fuel industry worked to obscure for decades. A collection of evidence just published to ClimateFiles.com reveals the extent to which oil companies and their trade associations sought to deny and downplay the relationship between climate change and extreme weather.
Nicky Sundt, a climate expert and former communications director for the U.S. Global Change Research Program during the George W. Bush administration, said she tried to publicly communicate the science behind that link, but was “stymied over and over again” by industry interests inside and outside the White House — an experience she has discussed with The Guardian and PBS Frontline.
“By interfering with the communications of climate science to the public, [the fossil fuel industry] knew that the public was less likely to become agitated and do something about it,” Sundt said. “The consequence was to slow efforts to reduce our emissions, and to leave us more unprepared for the impacts of climate change. The longer you wait, the more expensive it is to deal with all of these issues, and they’ve eaten up incredibly important time we needed.”
“A new norm”
In 1997, fossil fuel interests successfully convinced prominent United States officials to oppose U.S. ratification of the Kyoto Protocol — an international climate agreement that would have limited greenhouse gas emissions decades ago.
A year later, the American Petroleum Institute (API) — the largest oil and gas trade association in the U.S. — bluntly outlined a plan to keep drumming up opposition to the Kyoto Protocol as negotiations continued. According to a newly uncovered February 1998 internal strategy proposal reviewed by ExxonKnews, API would “develop and implement a campaign-style ‘rapid response’ team… to respond to op-eds that make exaggerated claims about climate science… and to media events staged by government officials and/or environmental organizations seeking to tie extreme weather events to possible human impacts on global climate.”
Long before that campaign began, internal industry memos and promotional materials show, major oil companies knew about the role that climate change would play in intensifying hurricanes, floods, droughts, heatwaves, precipitation patterns, and other extreme weather events.
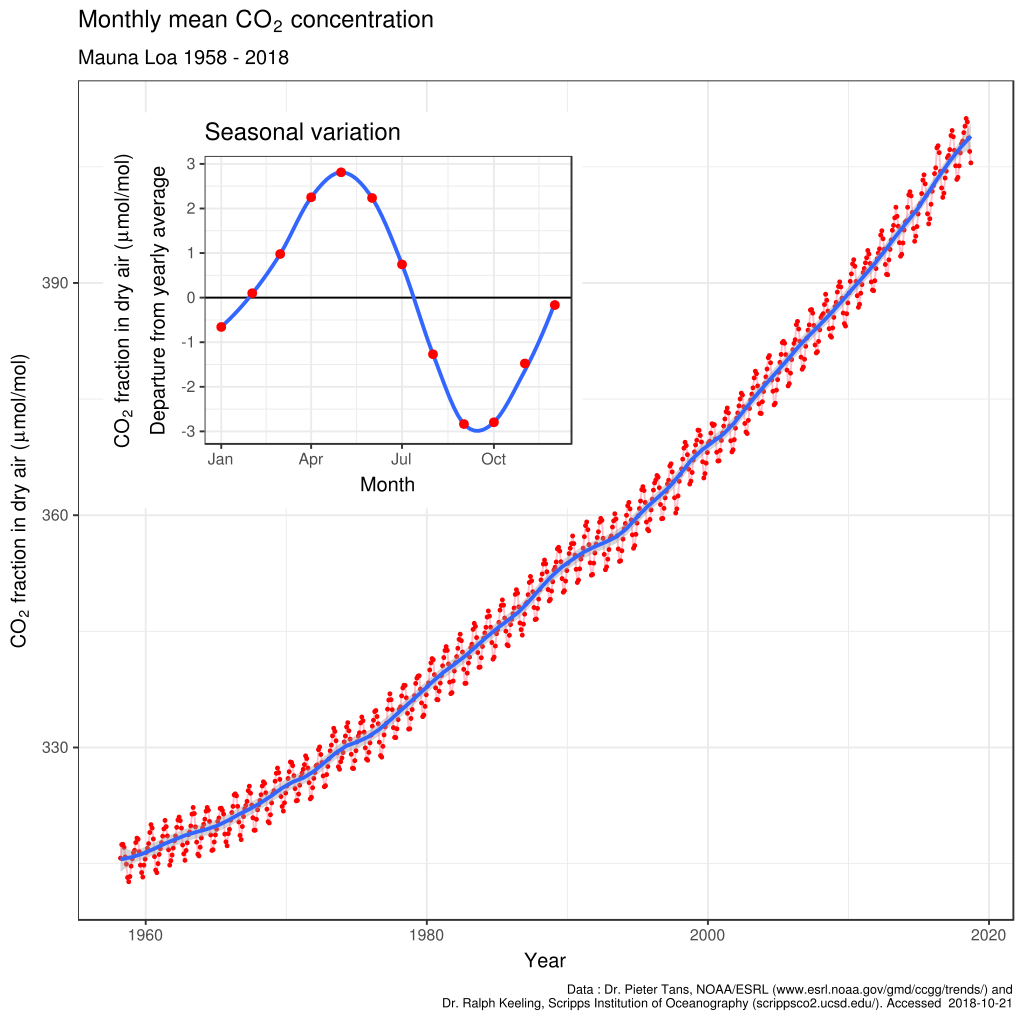
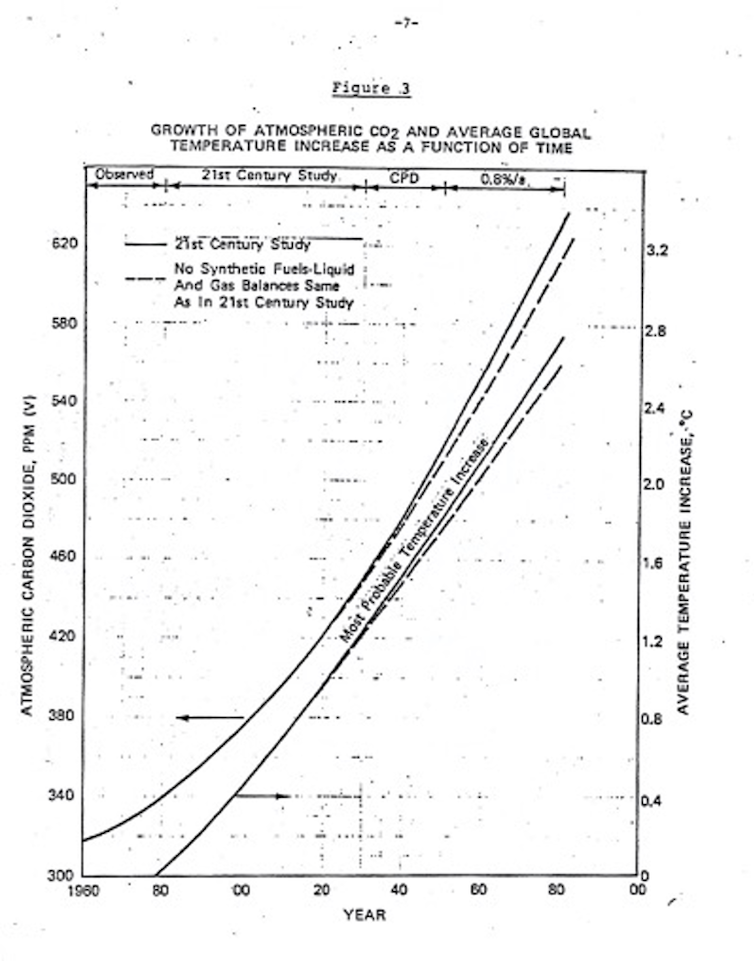
One 1979 memo distributed to Exxon management, about a report conducted by Steve Knisley of Exxon’s Research and Engineering Department, accurately predicted the growth of atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations by 2010 and referenced the “ecological consequences of increased CO2 levels.” Those consequences were listed in detail, including global temperature increases, water shortages in the U.S. southwest, increased rainfall, and “violent storms.”
In a 1991 film production by Shell, called “Climate of Concern,” a narrator warns that “if the weather machine were to be wound up to such new levels of energy, no country would remain unaffected,” and that “what is now considered abnormal weather could become a new norm.”
Another film produced that year by BP, called “This Earth – What Makes Weather?”, alludes to the ways climate change would increase the frequency and damage caused by extreme weather events like storms, flooding, and drought. “From warmer seas, more water would evaporate — making storms and the havoc they cause more frequent,” the narrator predicts. “Catastrophic floods could become commonplace and low-lying countries like Bangladesh would be defenseless against them.”
But around the same time, the industry began to worry about how public understanding of those phenomena could affect their core business. A 1989 presentation by Duane LeVine, a senior executive at Exxon, expressed concern that an extreme heat and drought event the year before had “drawn much attention to the potential problems and we’re starting to hear the inevitable call for action. Exactly what happens now is not clear… but this critical event has energized the greenhouse effort and raised public concern over PEG [potential enhanced greenhouse].”
Under the cover of trade associations and front groups, through PR campaigns and funded academic research, the industry developed a strategy to undermine the link between climate change and weather-related disasters — and discredit those who sought to communicate that science to the public.
A Campaign to Turn the Tide

One key player was the Global Climate Coalition (GCC) — an international industry lobbying group that was instrumental in early efforts to deny climate change and generate opposition to policy action to reduce emissions. In 1994, the GCC hired weather forecasting service AccuWeather Inc. to produce a report minimizing the impact of global warming on extreme weather, which the GCC would cite in a pamphlet distributed at the United Nations climate convention the following year.
“No convincing, observational evidence exists that hurricanes, tornadoes and other extreme temperature and precipitation events are on the rise because of the recent slight increase in the Earth’s surface temperature,” the report states.

In response to ExxonKnews’ requests for comment on the report, a spokesperson for AccuWeather said that “AccuWeather and the other leading consulting meteorologists involved had been engaged to produce an analysis based upon the available data at that time. There was much debate and uncertainty in the scientific community over the causes and effects of global warming during that time period, and a new generation of computer modeling studies was just beginning to emerge that would create an important shift in scientific judgment.”
“As an organization rooted in science, AccuWeather’s view on global warming and extreme weather has evolved over the past three decades, as has the view of many other scientific organizations,” they said, noting that data now shows a “marked increase in billion-dollar disasters due to extreme weather events.” Today, the spokesperson added, AccuWeather has signed the “Global Climate Science-Media Action Pledge”, and is committed to communicating the impacts of climate change on extreme weather to the public.
The GCC also hired academics to further their cause. Internal meeting notes from July 1997 show that the GCC commissioned a research paper from Robert E. Davis, a University of Virginia climatologist, explicitly denying the climate and extreme weather connection.

“A belief commonly held is that global warming will produce more extreme weather,” the published paper read. “While this thinking serves as convenient fuel for sensationalist headlines linking what only a decade ago would have been viewed as the normal vagaries of weather to some approaching climatic apocalypse, it is not based on sound science.”

In 1999, in the wake of Hurricane Floyd, Frank Maisano, then a spokesman for the GCC, faxed a memo to “Communicators Interested in Global Climate Issues.” “As millions of people flee Hurricane Floyd, many climate activists have again suggested — despite the facts — that hurricanes and global warming are connected,” the memo stated.
In response to questions about the memo and the GCC’s positions, Maisano told ExxonKnews that “Any fair review of the debate over any link between climate and severe weather has always been the subject of significant discussion between the experts themselves, especially with regard to hurricanes.”
“Importantly,” Maisano said, “GCC’s main focus at the time was on the economic impacts, sovereignty and effectiveness of any policy proposed to address climate change.”
Maisano now runs a strategic communications practice for Bracewell LLP, whose separate law practice provides services for oil and gas companies including Eni (currently being sued for climate deception in Italy) and Phillips 66 (which is a defendant in many U.S. climate lawsuits, including those filed by Bucks County and the state of New Jersey). Since 2005, the group has also advocated for renewables, Maisano said.
The industry’s campaign stretched on for years. In 2006, shortly after Hurricane Katrina, the DCI Group — a lobbying and campaign contractor with ties to Exxon — produced and sent VHS tapes of videos designed to look like a national news broadcast to Gulf of Mexico area news stations. The tape featured Dr. William Gray, a (now deceased) hurricane scientist at Colorado State University and climate change denier, stating that in the past 20 years, scientists had seen “no significant change in the frequency and intensity of major hurricanes around the globe…. This is the way nature sometimes works.” (Scientists have since concluded that climate-driven warming contributed to the increased rainfall and severity of storm surge during Hurricane Katrina, which killed nearly 2,000 people.)
According to Sundt, after Hurricane Katrina hit, the communications arm of the U.S. Global Change Research department proposed hosting a session on the implications for preparing for climate change on the Gulf Coast. “We had a well developed proposal, and it was just killed [by the White House] without explanation,” she said.
“A more resilient world”
Today, the steady growth of attribution science — or research investigating the role of climate change in altering or intensifying extreme weather events — has put a dent in Big Oil’s designs. The field of study has developed to even be able to tie the emissions of specific corporate actors to climate-worsened disasters — opening up more possibilities for those companies to be held liable for climate damages in court.
One such study, from researchers from the Union of Concerned Scientists and the University of California, Merced, found that nearly 40% of all forests burned in the Western U.S. and Canada since 1986 can be tied to emissions from just 88 of the world’s largest fossil fuel and cement manufacturers. That research was cited in Multnomah County’s lawsuit against oil and gas majors for climate damages last year.
Delta Merner, lead scientist for the Union of Concerned Scientists’ climate litigation hub and a co-author of the study, pointed out that many of the same companies that fought regulation of climate-warming emissions adapted their own fossil fuel infrastructure to account for rising seas, warming temperatures, and worsening storms decades ago.
“As you look through the oil industry’s own reactions to their knowledge about climate change, they were able to build better infrastructure to be resilient,” Merner said. “We would have a more resilient world, we would not be facing the realities of climate change that we’re seeing today if it wasn’t for the lies the industry propped up for so long.”
At least one oil major anticipated legal action decades ago. In a planning scenario from 1998, Shell made an eerie prediction: “In 2010, a series of violent storms causes extensive damage to the eastern coast of the U.S. … Following the storms, a coalition of environmental NGOs brings a class-action suit against the US government and fossil-fuel companies on the grounds of neglecting what scientists (including their own) have been saying for years: that something must be done.”
Shell was ahead of its time. Between the increased frequency, severity, and costs of extreme weather events, the advancing science connecting them to polluters, and mounting legal theories, Merner said she expects more communities to file suit. Even as she sees the industry’s deception evolving in content and sophistication — like companies trying to shift the blame for emissions onto consumers to avoid responsibility — Merner believes attribution research is evolving faster.
“It’s a testament to the power of science that climate litigation has been able to withstand an additional onslaught of disinformation from the fossil fuel industry and is now a key part in the fight for climate justice,” she said.
Note: Additional individuals mentioned here were asked to provide comment. The piece will be updated if they respond.
CLARIFICATION 4/3/24: This story has been updated to clarify the difference between Bracewell LLP’s strategic communication practice and its law practice.
Original article by Emily Sanders, ExxonKnews republished from DeSmog.