School’s out: how climate change is already badly affecting children’s education

Richard Juilliart/Shutterstock
Caitlin M Prentice, University of Oslo; Francis Vergunst, University of Oslo; Helen Louise Berry, Macquarie University, and Kelton Minor, Columbia University
Schools across South Sudan have been ordered to close as a heat wave of 45°C sweeps across the country. In recent years, severe flooding has already caused major disruptions to schooling in South Sudan where, on average, children complete less than five years of formal education across their lives.
As researchers interested in both climate change and learning, we’ve been surprised that most public debate in this area concerns how best to teach children about climate change as part of the curriculum. Recently, we examined a less discussed, but arguably much more consequential, question: How is climate change impacting children’s education worldwide?
In a recent paper published in Nature Climate Change, we reviewed studies linking climate change-related events or “climate stressors” to education outcomes. One of the clearest connections was between heat exposure and reduced academic performance.
A study in the US found that adolescents’ maths scores decreased significantly on days above 26°C. In China, hotter day-of-test temperatures were associated with a drop in exam performance equal to losing a quarter of a year – or several months – of schooling.
But it’s not just test days that matter. Studies show that raised temperatures also affect learning over longer time periods. For example, pupils’ test scores suffered when there were more hot days across the school year and even when the hotter weather occurred three to four years before exam day.
Our review also highlights how climate-related regional disasters like wildfires, storms, droughts and floods are keeping many children out of school entirely. Floods can prevent children from travelling to school and cause damage to school buildings and materials, which disrupts learning and lowers test scores.
In developing countries, storms and droughts commonly cause children to leave school permanently to join the workforce and support their families. Children in higher-income countries are not immune. They miss school days due to hurricanes and wildfires and these absences have measurable effects on education outcomes.
The impacts of climate disasters can also affect children before they are born with consequences that reverberate across their lives. For example, children whose mothers were pregnant during Hurricane Sandy were more likely to be diagnosed with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a condition that can make schooling more challenging.
In India, researchers found that raised temperatures lead to lower test scores due to crop failure and malnutrition, highlighting the importance of indirect links between climate stressors and subsequent school participation and learning.
Educational injustice
Our analysis suggests that climate change will exacerbate existing inequalities in global education access and attainment, with already disadvantaged groups facing the largest learning setbacks. In the US, heat had worse effects on exam scores for racial and ethnic minorities and children living in lower-income school districts.
Following a super typhoon in the Philippines, children whose families had fewer financial resources and smaller social networks were more likely to drop out of school than their better-resourced neighbours. In contexts where girls’ education is less prioritised than boys’, their school attendance and exam scores have suffered more following climate change stressors such as droughts and storms.
Globally, regions where people are more vulnerable to the effects of climate change – in terms of risk of harmful stressors occurring and resources available to adapt – are also regions where children already receive fewer years of schooling.
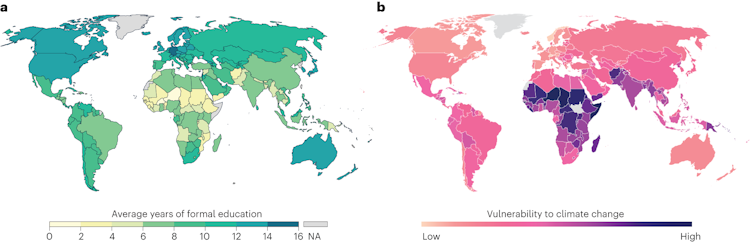
CC BY
The impacts of climate change on education are already widely visible. While the scale of the problem is daunting, there are many ways to take action. Most critically, global heating urgently needs to be limited by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases.
At the same time, children’s education must be protected from climate change stressors that are already occurring. Possible measures include installing cooling technologies, effective disaster response planning, building stressor-resilient schools and addressing systemic global inequalities related to socioeconomic, gender and racial discrimination.
Preventing harm to children’s education is a worthy goal in itself. But improving education can also contribute to greater awareness and climate literacy, while mitigating climate change and making children more resilient in the face of climate stressors.
Education can help fight climate change. But we must also fight climate change to prevent harm to education. Without action, the future of young people around the world hangs in the balance.![]()
Caitlin M Prentice, Postdoctoral Fellow, Department of Psychology, University of Oslo; Francis Vergunst, Associate Professor, Psychosocial Difficulties, University of Oslo; Helen Louise Berry, Honorary Professor, Centre for Health Systems and Safety Research, Macquarie University, and Kelton Minor, Postdoctoral Research Scientist, Computational Social and Behavioural Science, Columbia University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
