Charlie Gardner, University of Kent; Emily Cox, Cardiff University, and Stuart Capstick, Cardiff University
One recent Wednesday, while most scientists around the world were carrying out their research, we stepped away from our day jobs to engage in a more direct form of communication.
Along with more than 20 others from Scientists for Extinction Rebellion and assisted in our efforts by Doctors for Extinction Rebellion, we pasted scientific papers to the UK government’s Department of Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS). A group of us glued ourselves to the building, and nine scientists were arrested.
This kind of action may seem extreme for a scientist, but these are no ordinary times. As most members of the UK public now recognise, addressing the climate crisis requires drastic changes across society. In 2019, the UK parliament itself declared a climate emergency – and in an emergency, one must take urgent action.
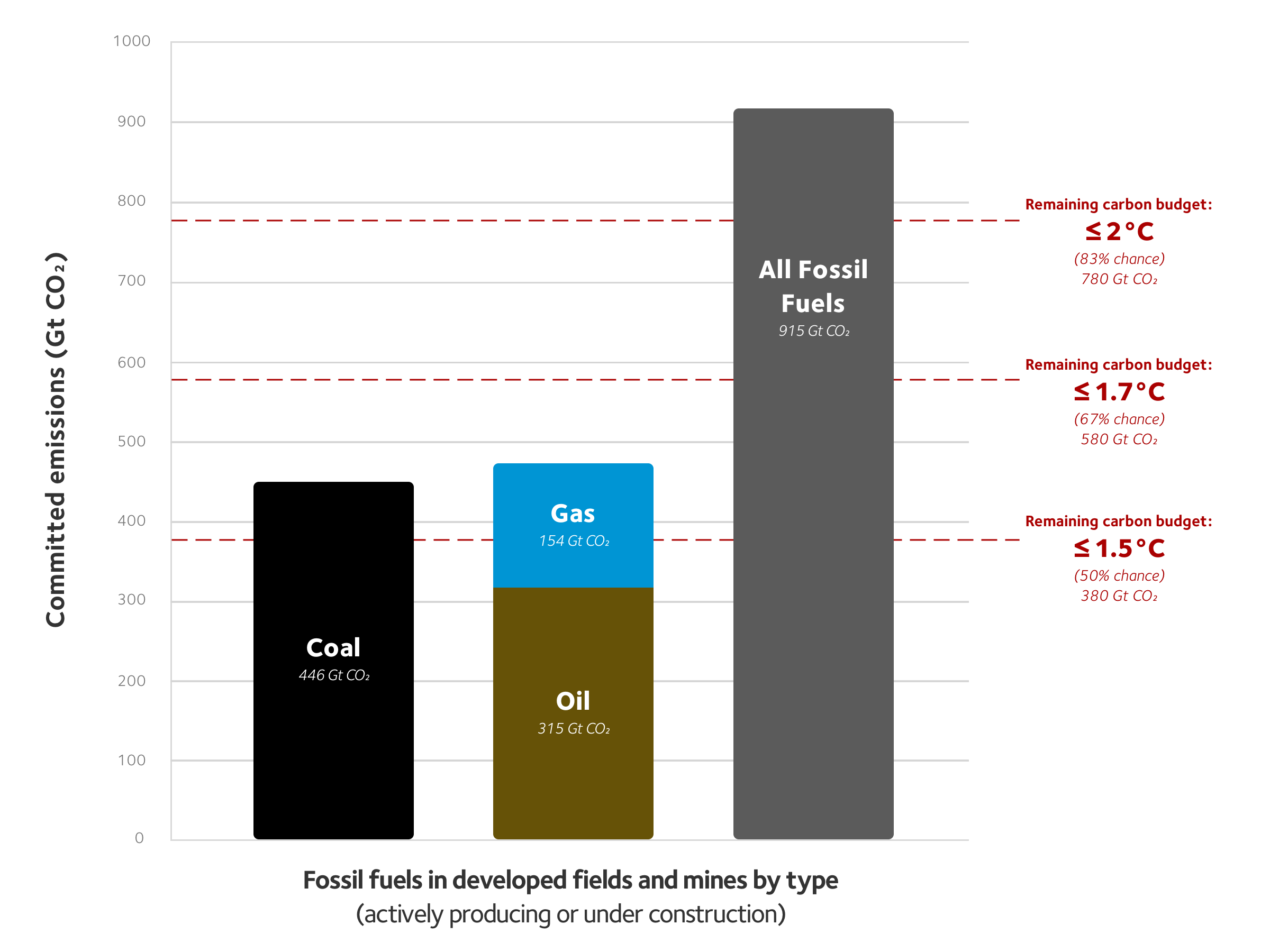
Seemingly endless academic papers and reports highlight the need for the immediate and rapid decarbonisation of the global economy if we are to avert climate change so serious that it risks the collapse of human civilisation. The International Energy Agency, a respected policy advisory body to countries around the world, warned in 2021 that “if governments are serious about the climate crisis, there can be no new investments in oil, gas and coal, from now – from this year”.
Prime Minister Boris Johnson has stated that “it is time for us to listen to the warnings of the scientists” on the climate emergency. But despite this, the UK government is choosing not to wind down the fossil fuel industry, but instead to expand it.
The government recently published its energy security strategy. However, rather than focusing on home insulation, energy efficiency and onshore wind as most experts suggest, the strategy promotes the expansion of oil and gas production.
Such measures do very little to address the pressing issues of rising fuel bills or heavy imports of Russian oil and coal. And as a self-proclaimed leader in global climate action, the UK’s doubling down on fossil fuels also sends a dangerous message to the rest of the world.
Evidence alone is easily ignored
In a choice between fossil fuels and a liveable planet, the government has chosen oil and gas. For scientists who have dedicated their lives to research, this is hard to take. Many of us do our work in the belief that, if we provide scientific information to decision-makers, they will use it to make wise decisions in the public interest.
Yet the global response to the climate crisis, despite decades of increasingly dire warnings, shows this to be naive. The reason is as simple as it is obvious: governments don’t respond to science on these matters, but to the corporate interests that invest so heavily in political donations and lobbying.
Scientists must face a difficult truth that doesn’t come easily to those of us who are most comfortable working diligently on experiments and journal articles: evidence alone, even if expertly communicated, is very easily ignored by those that do not wish to hear it.
If we are to help bring about the transition away from fossil fuels that the world so urgently needs, we are going to have to become much harder to ignore. This does not mean disregarding the evidence or abandoning our integrity: quite the opposite. We must treat the scientific warnings on the climate crisis with the seriousness that they deserve.
Become hard to ignore
History suggests that one of the most powerful ways to become hard to ignore – and one of the few options available to those who do not have deep pockets or the ear of politicians – may be through nonviolent civil disobedience, the refusal to obey certain laws in order to bring public and media attention to an unjust situation.
From universal suffrage to civil rights for people of colour and action on the Aids pandemic, many of the most progressive social changes of the 20th century were brought about in this way. Many would likely agree that such actions are morally justified in a planetary emergency.
The recent blossoming of environmental civil disobedience movements around the world, led by Extinction Rebellion and the Greta Thunberg-inspired youth strikes, has been hugely influential in changing the global conversation on climate. These movements have been linked to an unprecedented surge of public concern and awareness about the climate crisis.
The scientists arrested on that Wednesday included an expert in energy policy, an air pollution specialist, three ecologists and two psychologists, across all career stages from junior researchers to established professors. Some work on the planetary crisis itself, others on our societal responses to it, but none of us took our actions lightly.
Our understanding of our planetary peril obliges us to take action to sound the alarm, even if it means risking our civil liberties. And we are not alone. On April 6 more than 1,200 scientists in 26 countries participated in a global Scientist Rebellion, which included pasting scientific papers to the UK headquarters of oil giant Shell.
Civil disobedience doesn’t always need a particular target to be effective, because the main objective is to ring the alarm by generating media and wider public attention. Extinction Rebellion protests, for example, has targeted fossil fuel infrastructure, media and finance institutions and airports used by private jets, in addition to the general disruption caused by roadblocks.
But we went to BEIS because, as the government department responsible for climate change, it should be leading the transition away from fossil fuels. Instead, through enabling and promoting new fossil fuel extraction, it is doing the opposite.
Recent acts of law-breaking by scientists may seem radical, but the world’s most senior diplomat disagrees. On the release of the IPCC’s latest report, the UN Secretary General António Guterres said: “Climate activists are sometimes depicted as dangerous radicals. But the truly dangerous radicals are the countries that are increasing the production of fossil fuels.”
He could not have said it more clearly: while we scientists may have been breaking the law, it is the government that’s placing us all in danger.

Charlie Gardner, Associate Senior Lecturer, Durrell Institute for Conservation and Ecology, University of Kent; Emily Cox, Research Associate, Environmental Policy, Cardiff University, and Stuart Capstick, Senior Research Fellow in Psychology, Cardiff University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.